
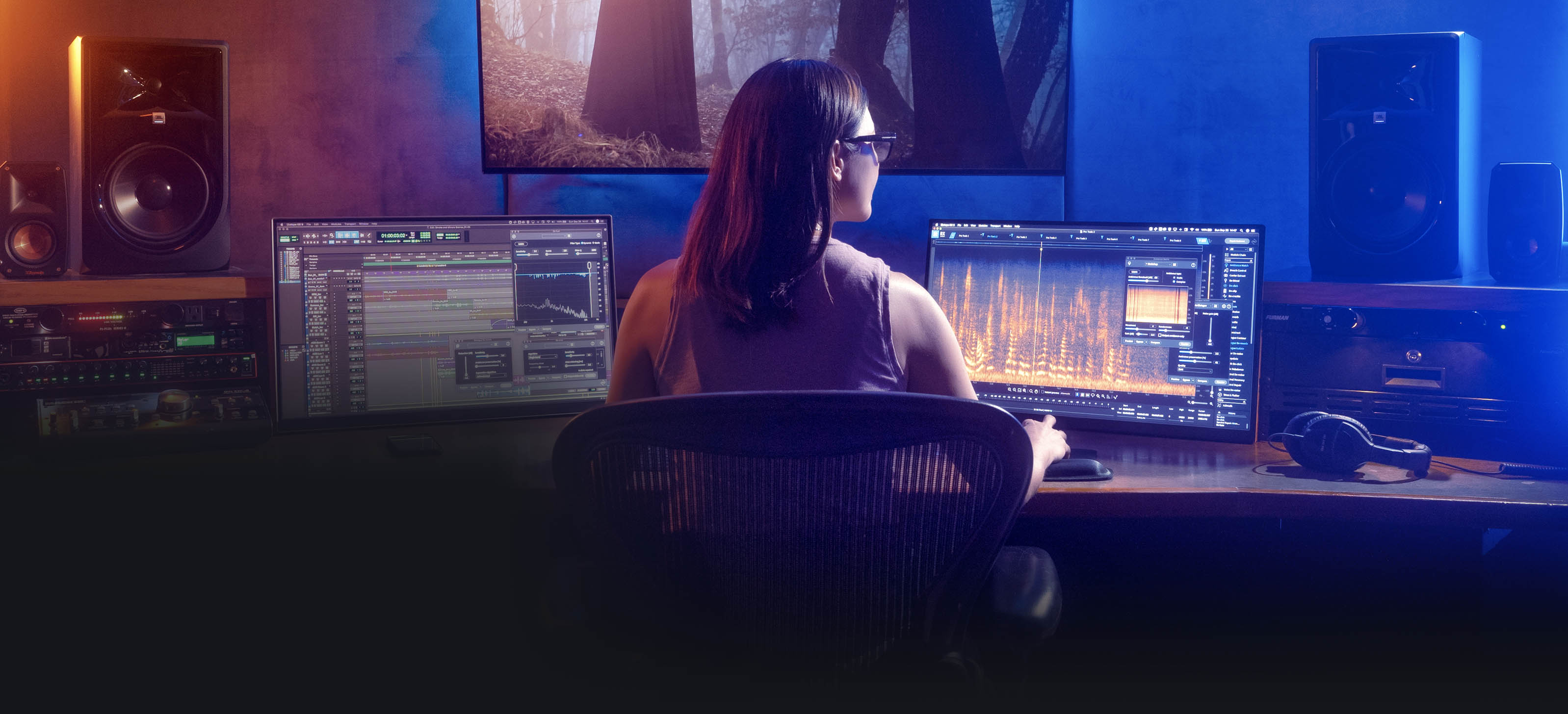
This is not really a review since I am not using every aspect of RX7 Standard and therefore not in the position to give a proper analysis, but rather it is how I am using in my own setup. That is what a sound engineer would be there for they worry about all the technical bits from distortion to mouth slaps and have the luxury of concentrating on just those things.
#Izotope rx 6 user guide series#
Post-limiter: Keeps true peak levels of the output signal below 0 dBTP to prevent any clipping from occurring.But this series of articles I have been writing is aimed at those working from home, possibly recording only their own books, and doing everything for themselves.Įven if you have a really, really good set up, you are producing yourself, and there is no hope you are going to catch every audio glitch while you are also performing your little socks off. Intermediate values between 0 and 1 produce so-called intermediate-phase filters that balance pre- and post-ringing while maintaining linear-phase response across a possibly wider range of frequencies. The value of 1 produces a linear-phase filter with a symmetric impulse response: the amount of pre-ringing is equal to the amount of post-ringing.

The value of 0 produces a minimum-phase filter, which has no pre-ringing, but maximal post-ringing. Pre-ringing: SRC filter pre-ringing amount in time domain (0 for minimum phase, 1 for linear phase, or anywhere in between).Īdjusts the phase response of the filter, which affects its time-domain ringing characteristic. At the same time, higher steepness of the frequency response requires a longer filter, which produces more ringing in time domain and energy smearing near the cutoff frequency.Ĭutoff shift: SRC filter cutoff frequency shift (scaling multiplier).Īllows shifting the filter cutoff frequency up or down, to balance the width of a passband vs. Higher filter steepness means better frequency performance of the filter: wider passband retains more useful signal, while stronger stopband attenuation provides better rejection of aliasing.Note about higher filter steepness values With iZotope SRC’s steep low-pass filter, users can completely avoid the common aliasing artifacts while maintaining the maximum frequency content. Aliasing can be heard as the frequencies in an inaudible range are shifted into an audible range, causing distortion and noise. Leaving frequencies above this point causes aliasing. When reducing the sampling rate, or downsampling, it is crucial to remove the frequencies that cannot be represented at the lower sampling rate. The highest frequency that can be represented accurately by a sampling rate is half of the sampling rate, and is known as the Nyquist frequency. For example, a 192 kHz audio sample can represent frequencies up to 96 kHz whereas a 44.1 kHz audio sample can only represent frequencies up to 22.05 kHz.
It is common to record and edit in high sampling rates since higher rates allow higher frequencies to be represented. Sample Rate Conversion (SRC) is a necessary process when converting material from one sampling rate (such as studio-quality 96 kHz or 192 kHz) to another rate (such as 44.1 kHz for CD or 48 kHz for video). The Resample module allows you to convert an audio file from one sampling rate to another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
